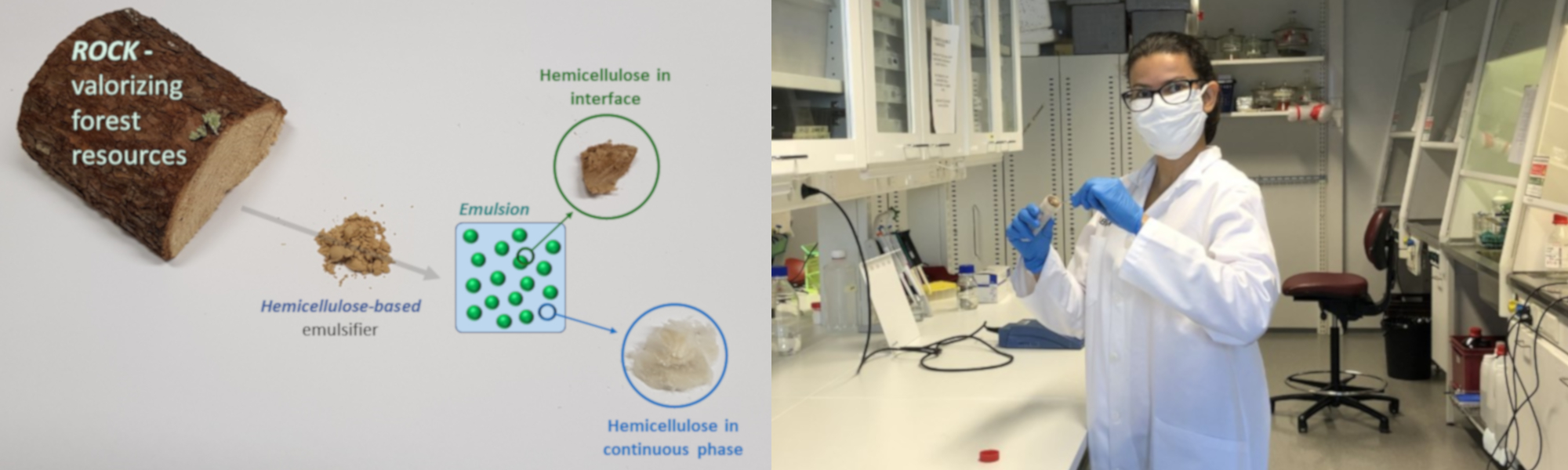
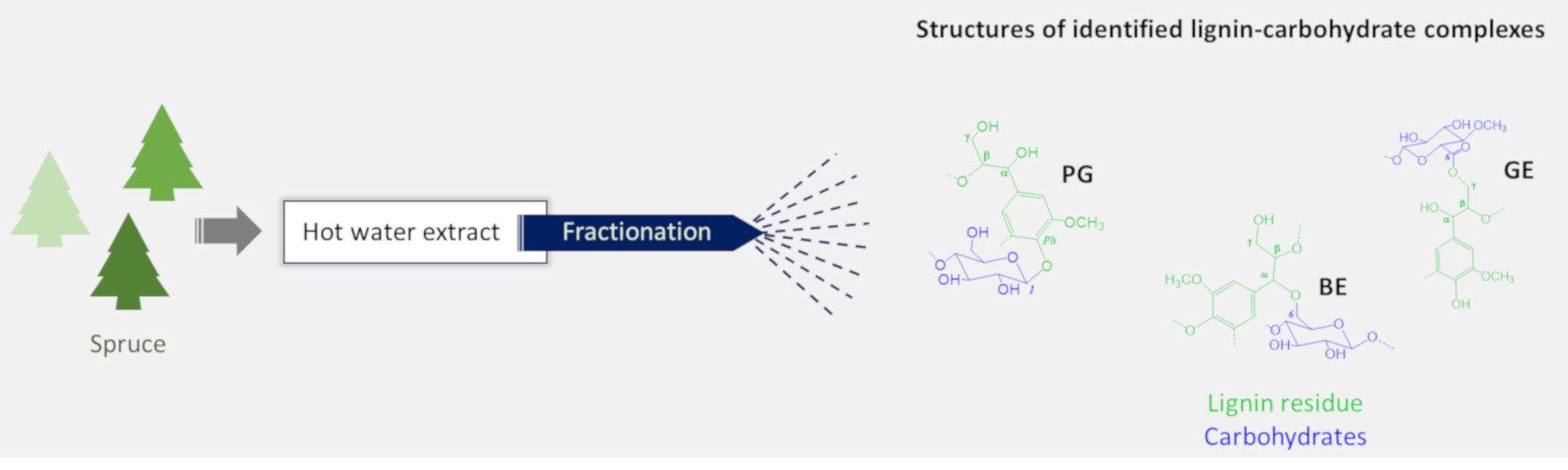
ROCK: ROle of lignin Carbohydrate complexes as Key to stable emulsions project has been completed. The project was designed to valorize forest resources, especially those from Nordic forests. Hemicelluloses-rich extracts, obtained by an environmentally-friendly water-extraction method was previously identified as a functional substance for stabilizing emulsions. Although rich in hemicelluloses, they also contain a certain amount of other polysaccharides and lignin co- extracted. When we commenced this project, the reason for the excellent stability performance of hemicellulose extracts as emulsifiers was still unclear and our hypothesis was that at least some of the residual lignins could be covalently linked to the polysaccharides forming so-called lignin-carbohydrates complexes (LCC). Such hybrid composites have two distinct regions, one more hydrophilic (hemicellulose part) and other more hydrophobic (lignin part). As a result, each region can interact with the different phases of the emulsion, possibly explaining the emulsion stability achieved using hemicellulose-based emulsifier. Our main aim was to investigate the presence of LCC in hemicelluloses extract and identify the role of such structures in emulsion stabilization. To do this we investigated the structures and functionalities of hemicelluloses extracts. In the initial part of this study, we characterized various types of hemicelluloses extracts obtained from birch and spruce wood. Using a combination of fractionation and advanced identification techniques, we demonstrated that some of the lignin residues in the extracts were involved in the formation of LCC linkages of various types (i.e., phenylglycoside, benzylether, and gamma-ester). A previous posted blog with these findings can be found here.
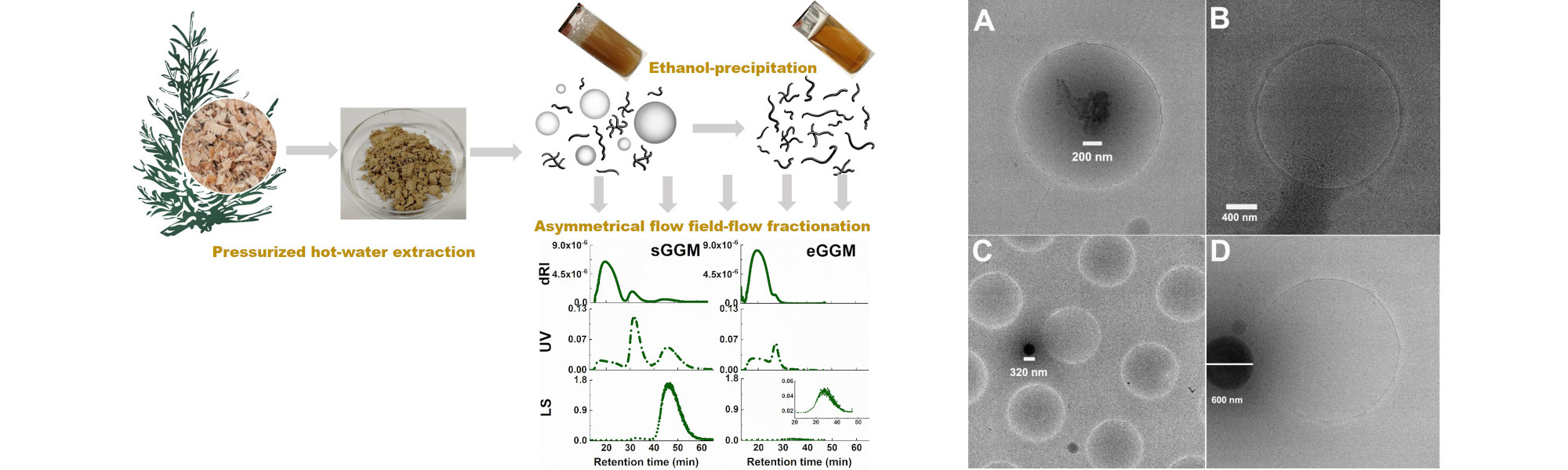
Next, we investigated how the different polymer populations in the hemicelluloses extract, including the LCC structures, are distributed between the emulsion phases (i.e., droplet interface and continuous phase) and what aspects drive such distribution. Beyond differences in the appearance (see figure), we discovered that the hemicelluloses populations in the various emulsion phases also differed in terms of their chemical and structural aspects. The residual lignin is a component of fundamental importance for the hemicelluloses orientation during emulsification and for the stability of the emulsions. Moreover, the various LCC structures identified in the hemicelluloses extracts were fractionated between emulsion phases depending of their type. In summary, ROCK provided the cornerstone to better understand the composition of hemicelluloses extracts and their functionality in emulsion, pushing the wood-hemicelluloses a step closer to added-value applications.
The ROCK project was funded by Tandem Forest Value and led by Assoc. Prof. Kirsi Mikkonen (University of Helsinki, Finland) and Prof. Martin Lawoko (Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden).