
All modern computers have more or less the same interfaces. There are some differences between desktop and laptop computers as well as various mobile devices, but usually all devices have at least the following interfaces (the letters refer to the images below). When you know the different connection ports, you know what devices you can connect to your computer.
AC power connector
The mains power connector is usually located on the back or side of the computer. There is a lot of variety in the shape and size of computer’s power connectors.
Display connector
The display connector is usually located on the back or side of the computer. As a rule, the connector is usually either one of two different connectors. If you are connecting a display to your computer, make sure that you have the appropriate connectors. You can handle most different pairs of connectors with the right adapter, but you will have to purchase them separately.
 Many computers have an HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface) port (the left port in the image) where you can connect e.g. a DVD or Blu-ray player, stereo amplifier or flat-screen TV. HDMI enables high-quality picture and audio transfer between connected devices.
Many computers have an HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface) port (the left port in the image) where you can connect e.g. a DVD or Blu-ray player, stereo amplifier or flat-screen TV. HDMI enables high-quality picture and audio transfer between connected devices.
Many computers have a DisplayPort interface (an alternative to HDMI; the right hand port in the image), where you can connect the computer display or a stereo amplifier, for example.
Local area network port (LAN)
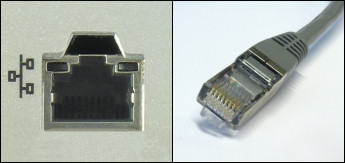
Use the Local Area Network (LAN) port to connect your computer to the Internet via a network cable. The LAN socket and cable are easy to recognize due to their special appearance.
USB port

Devices that can be connected to the USB port include the mouse, keyboard, digital camera, USB flash drive, scanner etc. There are several versions of the USB port. You can also charge various devices by connecting them to the computer through the USB port. The image on the right shows two regular, rectangular USB-A ports and a suitable plug.
The small micro-USB port has been the most common port in phones, cameras and other portable devices for a long time.
 The newer USB-C port (picture on the right: Wikimedia Commons/Bandideux) is becoming increasingly common.
The newer USB-C port (picture on the right: Wikimedia Commons/Bandideux) is becoming increasingly common.
You can tell the port and its connector by their small size, rounded shape, and by the fact that it can be connected either way around.
 The Lightning connector, common in Apple products, can be connected to the USB port with an adapter or a separate cable with the correct plugs.
The Lightning connector, common in Apple products, can be connected to the USB port with an adapter or a separate cable with the correct plugs.
Audio ports
You can connect external speakers, headphones, or a microphone to a computer. Headphones, for example, can be connected to the computer through a USB port (above) or a round 3.5-millimetre plug.
 In mobile devices and computers which are a few years old at most, the same port can be used to convey audio signal in and out of the device e.g. to and from headphones equipped with a microphone. Pictured right is such a combination audio port on a Mac computer (despite the ‘regular headphones’ symbol next to it).
In mobile devices and computers which are a few years old at most, the same port can be used to convey audio signal in and out of the device e.g. to and from headphones equipped with a microphone. Pictured right is such a combination audio port on a Mac computer (despite the ‘regular headphones’ symbol next to it).
Other ports
Some laptops have expansion card slots. An ExpressCard (EC) slot accepts many kinds of devices, and to a Secure Digital (SD) slot you can insert e.g. an SD or MicroSD camera memory card for fast transfer of digital photos.
Wireless network connections
With the exception of desktop computers, all modern devices can connect to wireless networks. Wireless connectivity models include:
 WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network): with WLAN you can connect your computer at home or at the university to a wireless network such as the university network Eduroam (more on wireless networks at UH). A WLAN network covers an area that typically ranges from some tens of metres to some hundreds of metres.
WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network): with WLAN you can connect your computer at home or at the university to a wireless network such as the university network Eduroam (more on wireless networks at UH). A WLAN network covers an area that typically ranges from some tens of metres to some hundreds of metres. Bluetooth networks: Using Bluetooth, you can create a short-range connection between, say, a laptop computer and a mobile phone or headphones. This way you can transfer data from the computer to the phone or vice versa. In order to use a Bluetooth network both the devices need to support Bluetooth. The range of the network does not exceed some tens of metres. To connect a device to a Bluetooth network, turn on the Bluetooth functionality on the device.
Bluetooth networks: Using Bluetooth, you can create a short-range connection between, say, a laptop computer and a mobile phone or headphones. This way you can transfer data from the computer to the phone or vice versa. In order to use a Bluetooth network both the devices need to support Bluetooth. The range of the network does not exceed some tens of metres. To connect a device to a Bluetooth network, turn on the Bluetooth functionality on the device.
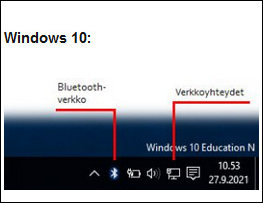
If you are having trouble connecting to a LAN or WLAN on your computer, you can check their status as follows:
- Windows: Click the network connections icon in the notification area in the lower right-hand corner of the screen (see the image above). This will show you the network connections available to your computer and their current status. If you cannot see the icon, click the triangle-shaped Show hidden icons button in the notification area.